Page 329 - Universitas Terbuka di Era Informasi
P. 329
UNIVERSITAS TERBUKA DI ERA INFORMASI
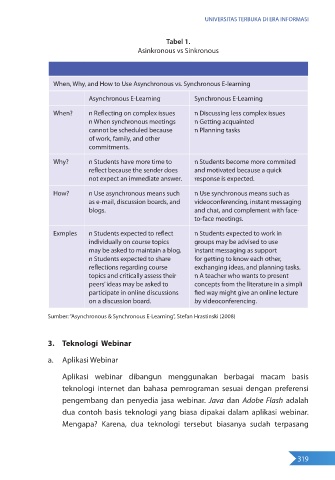
Tabel 1.
Asinkronous vs Sinkronous
When, Why, and How to Use Asynchronous vs. Synchronous E-learning
Asynchronous E-Learning Synchronous E-Learning
When? n Reflecting on complex issues n Discussing less complex issues
n When synchronous meetings n Getting acquainted
cannot be scheduled because n Planning tasks
of work, family, and other
commitments.
Why? n Students have more time to n Students become more commited
reflect because the sender does and motivated because a quick
not expect an immediate answer. response is expected.
How? n Use asynchronous means such n Use synchronous means such as
as e-mail, discussion boards, and videoconferencing, instant messaging
blogs. and chat, and complement with face-
to-face meetings.
Exmples n Students expected to reflect n Students expected to work in
individually on course topics groups may be advised to use
may be asked to maintain a blog. instant messaging as support
n Students expected to share for getting to know each other,
reflections regarding course exchanging ideas, and planning tasks.
topics and critically assess their n A teacher who wants to present
peers’ ideas may be asked to concepts from the literature in a simpli
participate in online discussions fied way might give an online lecture
on a discussion board. by videoconferencing.
Sumber: “Asynchronous & Synchronous E-Learning”, Stefan Hrastinski (2008)
3. Teknologi Webinar
a. Aplikasi Webinar
Aplikasi webinar dibangun menggunakan berbagai macam basis
teknologi internet dan bahasa pemrograman sesuai dengan preferensi
pengembang dan penyedia jasa webinar. Java dan Adobe Flash adalah
dua contoh basis teknologi yang biasa dipakai dalam aplikasi webinar.
Mengapa? Karena, dua teknologi tersebut biasanya sudah terpasang
319