Page 65 - Reimagining Higher Education : Case Studies On Designing For Inclusion, Equity, And Access In The Buka Project
P. 65
H. K. Dharam Singh et al. · Empowering educators through the authentic experience of
creating open educational resources - Open University Malaysia (OUM), Malaysia
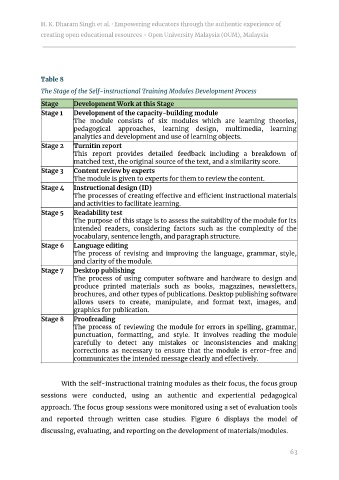
Table 8
The Stage of the Self-instructional Training Modules Development Process
Stage Development Work at this Stage
Stage 1 Development of the capacity-building module
The module consists of six modules which are learning theories,
pedagogical approaches, learning design, multimedia, learning
analytics and development and use of learning objects.
Stage 2 Turnitin report
This report provides detailed feedback including a breakdown of
matched text, the original source of the text, and a similarity score.
Stage 3 Content review by experts
The module is given to experts for them to review the content.
Stage 4 Instructional design (ID)
The processes of creating e ective and e cient instructional materials
and activities to facilitate learning.
Stage 5 Readability test
The purpose of this stage is to assess the suitability of the module for its
intended readers, considering factors such as the complexity of the
vocabulary, sentence length, and paragraph structure.
Stage 6 Language editing
The process of revising and improving the language, grammar, style,
and clarity of the module.
Stage 7 Desktop publishing
The process of using computer software and hardware to design and
produce printed materials such as books, magazines, newsletters,
brochures, and other types of publications. Desktop publishing software
allows users to create, manipulate, and format text, images, and
graphics for publication.
Stage 8 Proofreading
The process of reviewing the module for errors in spelling, grammar,
punctuation, formatting, and style. It involves reading the module
carefully to detect any mistakes or inconsistencies and making
corrections as necessary to ensure that the module is error-free and
communicates the intended message clearly and e ectively.
With the self-instructional training modules as their focus, the focus group
sessions were conducted, using an authentic and experiential pedagogical
approach. The focus group sessions were monitored using a set of evaluation tools
and reported through written case studies. Figure 6 displays the model of
discussing, evaluating, and reporting on the development of materials/modules.
63